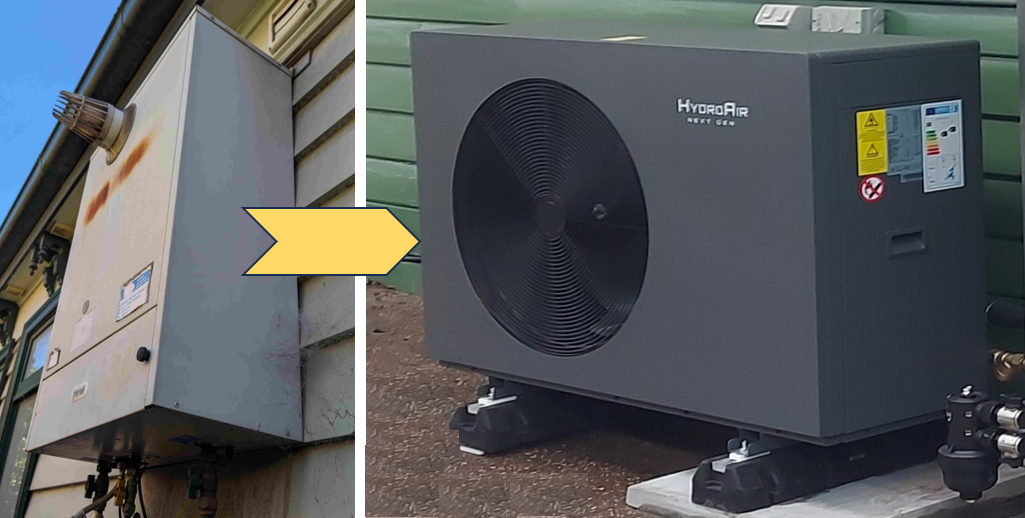

Gas Boiler to Heat Pump
Replace your gas boiler with a hydronic air-to-water heat pump for operating savings using your solar power. Also, contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Common questions
- Can it be done?
- What does it cost?
- Will it work with my radiators?
- When should I change over my gas boiler?
- Do I have enough space for a heat pump?
- How does the cooling work?
- Do I have to upgrade my power?
Answers
- Yes, it can be done. Hydrosol has been involved in many successful projects where clients have replaced their gas boiler with an air-to-water hydronic heat pump.
- For best results, improve the thermal performance of your home to reduce your heating load. This makes the task of the heat pump easier, using less power from your solar panels.
- For example: Brunswick, Ascot Vale
Cost
- A hydronic heat pump, buffer tank and fittings will cost around $15k for an average home plus installation.
- A modern condensing gas boiler will cost around $5k plus installation.
- Expect to recover the difference by using your own solar power. Also, your heat pump will last longer, be safer and add value to your home.
Radiator Temperature
- Consider a high-temperature hydronic heat pump that can heat water to 75 degrees. This will certainly work with your existing radiator panels.
- However, your radiator panels may be operating closer to 60 degrees. If you have been working on improving thermal performance, your heating load will be less and your radiator panels can be set lower.
When to Upgrade
- Replace your gas boiler after 10 to 15 years, which is its typical life span. If older than this, it may be operating inefficiently or may even be unsafe and leaking gas.
- In our experience, a well maintained heat pump can last more than 20 years.
- Check your winter gas bills for gas usage and operating costs. Compare that with the previous two years. If it has been increasing, it may be time to change it over.
- If you are doing a renovation or extension, that is an ideal time to make the change. Identify the heating load of your new home. Match your new heat pump to your largest heating load, typically in July.
Heat Pump Location
- The best location for your hydronic heat pump is where your gas boiler is currently located to access existing water flow and return pipes located there.
- If this location does not allow for good airflow through the evaporator coils, then install the buffer tank where your gas boiler is. Then install the heat pump in a better location.
- Consider a nearby location for your heat pump on the ground, raised up or on your roof for better airflow.
- The outlet air should not feed back to the inlet side otherwise this will reduce operating efficiency.
Heat Pump Cooling
Most hydronic heat pumps give you a cooling option in reverse cycle. It cools the hydronic water and absorbs heat inside your house.
However, cooling does not work with radiator panels. You need a convector circuit or underfloor hydronic circuits.
If you have radiator panels, consider adding an additional fan-coil convector circuit.
If you have underfloor heating circuits, ask whether your hydronic heat pump can provide area cooling in summer.
Explore multiple hydronic circuits for your heat pump:
- Underfloor heating and cooling
- Fan-coil convector heating and cooling
- Radiator panel heating only
Latent Cooling
Your heat pump can produce chilled water as low as 7 degrees. This will produce condensation in your convector that is drained outside to reduce humidity inside. The process behind this is latent cooling.
Area Cooling
Your heat pump can produce a comfortable floor temperature above the dew point of around 18 degrees. Whilst this is not as effective as convector cooling with chilled water, you can make it work. Consider these points:
- The larger the surface area, the better
- Reduce your heat load by improving the thermal performance of your house
- Improve shading to remove sunshine radiation through windows
- Use fans to reduce the perceived temperature, ceiling fans are best
Heat Pump Power
Check the power supply coming into your home:
- Is there sufficient power for new heat pumps, induction cooktop and other appliances?
- How about power for an electric vehicle as well?
- Is it 1-phase or 3-phase, what should it be going forward?
- Will your switchboard support these additional appliances?
- Do you need to upgrade your power?
- For a renovation or new build, consider power supply at the design stage.
- To reduce power bills with the new demand tariff, run your discretionary electrical appliances across the day, outside of peak times.
Tips
- Set your boiler to less than 60 degrees and monitor its effectiveness. A lower temperature will be make your heat pump more efficient, be safer with toddlers and less wearing on furnishings.
- Turn down your radiator panels as you work on improving the thermal performance of your house. Every step you take will improve your operating costs.
- Reduce your night-time temperature settings from day-time.
- Install thermostatic heads on your radiator panels in rooms so they automatically adjust to your settings.
- Zone your bedrooms to be cooler than your Living/Dining/Kitchen or home-office areas. Turn off radiator panels in unused rooms.
Energy Objective
Aim for a 7-Star energy rating for your home. This will reduce your heating and cooling load. Contact us about a staged improvement plan.
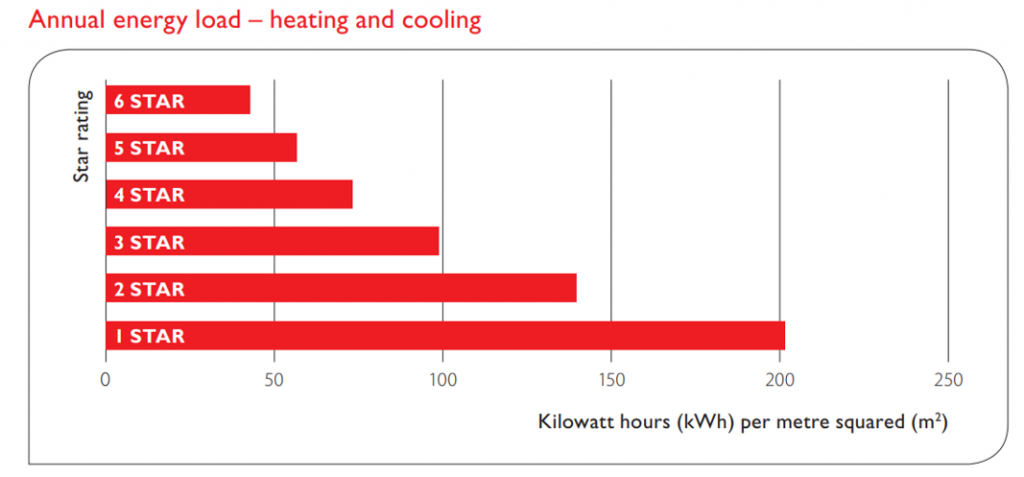
The horizontal bar graph shows the significant reduction in energy demand by improving thermal performance. Each higher Star Rating reduces energy use by between 22% and 31%.
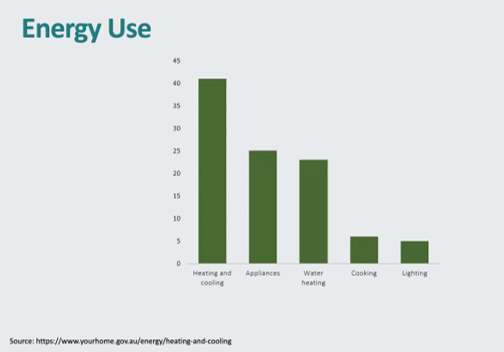
The vertical bar graph shows that heating and cooling is about 40% of your energy demand.
Benefits
- Lower heating and cooling running costs
- Smaller and less expensive heat pump
- More effective use of your solar power
- Adds value to your house
